Where is Blockchain Data Stored?
PUBLISHED
- February 3, 2023
- 12:57 am
PUBLISHED
- February 3, 2023
- 12:57 am

Blockchain technology is a decentralized, distributed ledger that keeps track of all transactions made on its network. Unlike a traditional database, where data is stored in a central location, data in a blockchain network is stored in multiple nodes that are spread out across the network. But where exactly is this data stored, and how does it ensure the security and integrity of the blockchain?
LIKE THIS
A Network Of Identical Copies

The answer to these questions lies in the way blockchains are designed. Unlike a traditional database, which has a single point of control, a blockchain network is made up of a network of nodes, each of which has a copy of the entire blockchain. This means that there is no central point of control, and no single point of failure. Instead, the network is designed to be self-governing, so that transactions are validated and processed by a consensus mechanism that involves multiple nodes.
In order to ensure the integrity of the blockchain, data is stored in multiple nodes at once. This ensures that if one node is compromised, the other nodes will still have a copy of the blockchain, and will be able to continue processing transactions. This also ensures that the data stored in the blockchain is secure and tamper-proof, as it would be very difficult for an attacker to alter the data in multiple nodes simultaneously.


When a transaction is made on a blockchain network, it is broadcast to all of the nodes in the network. Each node then verifies the transaction, and if a consensus is reached that the transaction is valid, it is added to the blockchain. This process of adding transactions to the blockchain is known as mining, and it is performed by nodes known as miners. Miners are incentivized to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain, as they receive rewards in the form of cryptocurrency for their efforts.
Blockchain Security and Encryption
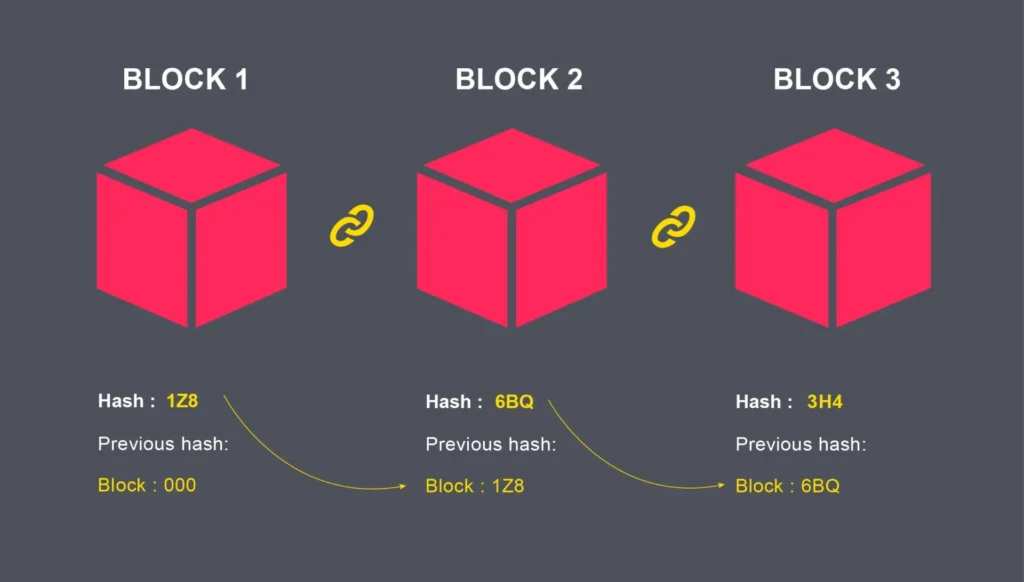

In addition to mining, blockchains also employ other security mechanisms, such as cryptographic algorithms, to protect the integrity of the data stored in the network. For example, blockchains often use digital signatures, which allow users to sign transactions, and public-private key pairs, which allow users to encrypt and decrypt data. These security mechanisms ensure that the data stored in the blockchain is secure and tamper-proof, even if an attacker is able to gain access to a node in the network.
Using this network of identical nodes, blockchain technology provides a decentralized, distributed ledger of all transactions made on its network. This ensures that the data stored in the blockchain is transparent and publicly accessible, and that the network is resistant to censorship and tampering. However, this also means that blockchains can be slow and expensive to process transactions, as the consensus mechanism that is used to validate transactions requires multiple nodes to reach agreement.


In order to address these issues, blockchain designers are exploring alternative consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Stake, which is faster and more energy-efficient than the current system, Proof of Work. Additionally, blockchains are also exploring ways to scale the network, such as sharding, which would allow transactions to be processed in parallel, rather than serially.
So, in essence, the data stored in a blockchain network is stored in multiple nodes that are spread out across the network. This ensures the security and integrity of the blockchain, as it would be very difficult for an attacker to alter the data in many nodes simultaneously. Blockchains are continuously exploring ways to improve the security and efficiency of their networks, and it will be interesting to see how they evolve in the coming years.